Business investors are often looking for ways to make tax-efficient investments. The most in-the-know investors will diversify their investment portfolios with at least one SEIS UK company or EIS UK company.
But what is SEIS? Or EIS? SEIS stands for Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme. EIS stands for Enterprise Investment Scheme. These are schemes created by the UK government, which gives a tax break to investors. They get the tax break by investing in high-risk companies in their early stages.
To get the benefits of SEIS and EIS investments, you’ll need to make sure the company and shares are eligible for the SEIS and EIS. You will also need to be eligible yourself for these initiatives. Otherwise, you may not receive the tax breaks you’re expecting.
To make yourself and your startup more attractive to investors, you can use SEIS and EIS. People are much more likely to invest in your startup if they know it will make them SEIS and EIS eligible. That’s exactly why the government created the schemes.
It is part of their way of supporting SMEs in the UK. The UK government realized that one of the barriers for startups was getting the funds needed to expand. That’s why they created the SEIS and EIS.
What is SEIS?
Are you wondering what is SEIS? As mentioned above, SEIS stands for Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme. The government created it in the UK in 2012. The purpose was to get more investors interested in investing in UK-based startups.
The way it works is by giving tax relief to those investors who qualify for the SEIS. They must subscribe to shares within eligible companies. To assess if a company comes under the SEIS, companies or investors can contact HMRC to find out.
The tax relief may be up to 64% with this scheme. The SEIS investors must be helping small companies in the early stages.
If you’re a startup owner looking for investors, it could help greatly to become part of the SEIS or EIS. It could make investing in your business much more attractive. If you’re an investor, it’s worth looking into these schemes.
Benefits
SEIS provides the following great benefits:
- You could have tax relief of up to 50% against the amount you invested
- You could be exempt from Capital Gains Tax (CGT) when you sell your shares. This is if you’ve had the shares for at least three years.
- If in the same tax year, CGT write-off of 50% of the amount invested
- If the shares are held for more than two years, they are usually free of inheritance tax (IHT)
- If you have to sell your shares at a loss, you could offset this against Income Tax or CGT.
- The investor may take back some or all of the money invested in the preceding year of investment
The Criteria for SEIS Eligibility
What are the requirements to be eligible for SEIS as an investor?
- The maximum amount of investment in any amount of qualifying businesses is£100,000.
- You need to keep the shares for at least three years. If you don’t, you will experience relief clawback.
- Your SEIS tax relief cannot be carried forward.
- You need to be a taxpayer in the UK.
What is EIS?
So, then what is EIS? As described, EIS stands for Enterprise Investment Scheme. It goes along with the SEIS but helps more established companies. The goal is still to attract more investors.
EIS companies offer a few types of tax relief to investors. They may be direct investors or those through an EIS fund or portfolio service. Again, it must be an EIS eligible company invested in by an EIS eligible investor.
EIS is designed to help grow established companies. On the other hand, SEIS targets smaller companies that’ve only just started.
EIS has been around since 1994. The idea of the UK government was that new businesses could use SEIS when they are at the proof of concept stage. Then they can move on to SEIS when they hit the seed round.
Benefits

EIS provides the following great benefits:
- Capital Gains Tax (CGT) exemption is given to the sale of shares, ensured the investor kept them for at least three years.
- It’s possible to defer all their investment against CGT incurred either up to 1 year before or three years following disposal
- The shares must be held for two years, and then they are usually inheritance tax (IHT) free
- Shares can be offset against Income Tax or CGT if sold at a loss.
- It’s possible to take back some or all of an investment in the preceding year of investment.
The criteria for EIS eligibility
What are the requirements to be eligible for EIS as an investor?
- The maximum investment is £1 million in any amount of eligible companies, in each tax year.
- Shares must be held for at least three years. If you don’t adhere to this, you will experience relief clawback.
- Your EIS tax relief cannot be carried forward.
- You must be a taxpayer in the UK.
- You can’t have a connection with the EIS company. A connection is defined as either being an employee, partner, or paid director.
- You can’t be buying the shares from the market; they need to be new.
SEIS vs. EIS – what’s the difference?
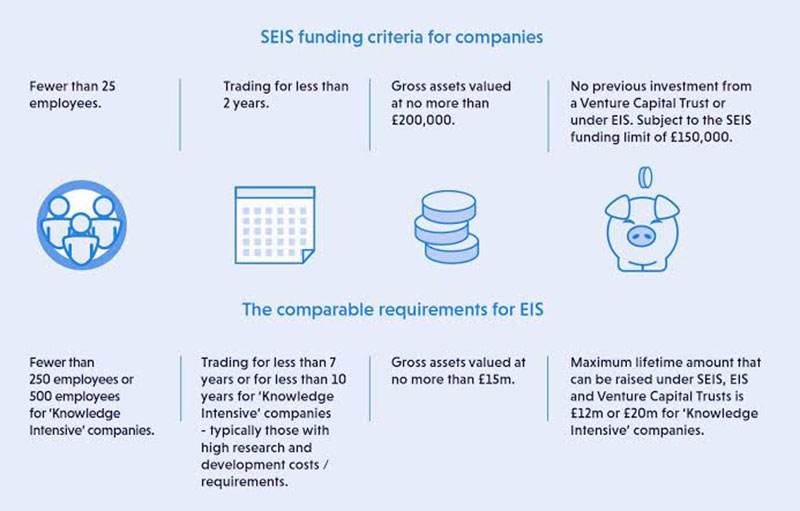
Image source: Angelsden
SEIS vs. EIS – they do have similarities. They are similar in the fact that they have the same purpose. To help early-stage companies attract investment. So, what’s the difference between EIS and SEIS? EIS companies are later-stage businesses. SEIS focuses on earlier stage companies.
Through SEIS, early-stage companies can attract investments up to £100,000 per tax year. The investor could get a 50% tax break on this. The investor would also enjoy an exemption from capital gains tax on profits from the sale of their shares. This is provided that they wait three years to sell the shares, whereas EIS focuses on startups of medium size. The investor could invest up to £1 million per tax year. This would get them a 30% tax break, and they get the same benefit as with SUIS of capital gains tax exemption on share sale profits. Again, provided that they kept the shares for at least three years.
Startups looking for investors for money could become more attractive if they qualify for SEIS or EIS. The tax relief for investors can be a big drawcard towards investing in your company. If you’re an investor, get to know EIS and SEIS. This could help you make excellent investments with more benefits for you. It’s important to note that SEIS investment will give you more tax relief; this is because it is riskier.
There are a few companies that will qualify for both SEIS and EIS. In this case, the first investors will get SUIS, and once that allowance is up, other investors will get EIS. You’ll get an email confirming which you qualified for, SEIS or EIS.
FAQs about SEIS and EIS
1. What are SEIS and EIS?
The UK government offers tax incentive programs called SEIS (Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme) and EIS (Enterprise Investment Scheme) to promote investments in high-risk, early-stage businesses.
Investors who put money into qualifying businesses can receive tax benefits from SEIS and EIS.
2. What are the benefits of SEIS and EIS for investors?
Significant tax benefits are available to investors, which can help to lower overall investment risk.
Investors may receive up to 50% of their original investment via SEIS, compared to 30% under EIS. Moreover, capital gains tax (CGT) relief is offered by SEIS and EIS, which can improve investment returns still further.
3. What kind of companies are eligible for SEIS and EIS?
Early-stage and high-risk companies are the target of SEIS and EIS. Companies must operate a qualified trade and have a permanent establishment in the UK to be eligible.
Also, SEIS and EIS must have fewer than 25 workers and gross assets of no more than £200,000 and £15,000,000, respectively.
4. What is the maximum amount of investment allowed under SEIS and EIS?
The maximum investment allowed under SEIS is $100,000 each tax year, whereas it is $1,000,000 under EIS.
The amount that can be invested in a single company and the overall amount for which tax relief can be claimed are subject to additional restrictions.
5. Can an investor claim tax relief for investments made under SEIS and EIS?
Indeed, under both SEIS and EIS, investors may claim tax reduction on their investments in qualified enterprises.
The plan and the investor’s individual tax condition both influence the amount of tax benefit.
6. What are the key differences between SEIS and EIS?
The amount of tax relief given, the maximum investment amount, and the size of the firm that is qualified are the primary distinctions between SEIS and EIS.
Smaller, early-stage businesses are the target of SEIS, while more established, high-risk businesses are the target of EIS.
7. How can a company apply for SEIS and EIS?
A corporation must first make sure it satisfies the qualifying requirements before applying for SEIS and EIS.
The application must then be completed and submitted to HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) for approval. After approval, the business can start soliciting capital from investors.
8. What are the risks associated with investing in SEIS and EIS eligible companies?
It can be risky to invest in early-stage and high-risk businesses, and investors should be ready to lose some or all of their money.
The tax reduction provided by SEIS and EIS may also be altered or eliminated in the future.
9. Are there any restrictions on the use of the funds raised through SEIS and EIS?
Indeed, there are limitations on how the money generated through SEIS and EIS can be used.
There are restrictions on the amount of funds that may be used for specific activities, such as the purchase of real estate or investments in other businesses, and they must be utilized to execute a qualifying deal.
10. Can an investor sell their SEIS or EIS shares?
Although there are limitations on when and how this can be done, investors may sell their SEIS or EIS shares.
To be eligible for the tax break, the shares must be held for at least three years, and there can be limitations on the price at which they can be sold.
Ending thoughts on SEIS and EIS
If used correctly, SEIS and EIS can be excellent ways of attracting investors. Entrepreneurs and expanding businesses can use these to encourage investment. Investors enjoy these schemes for tax breaks. The investments could raise more money, which is a better outcome for the investor.
Investor Relations (IR) is a vital part of any corporate website, along with the other “Big 4”. The big 4 are Public Relations (PR), About Us, and Employment. For both startups and potential investors, this is critical to know. Investors expect to go to a company website and be able to find a section on investor relations.
When investors are researching your site, you want it to look as professional and trustworthy as possible. This means you need to get the right info on your website as well as an engaging design. Web development companies like TMS can make you a high-quality site. They offer economical solutions for any needs you have concerning business web development.
If you enjoyed reading this article on SEIS and EIS, you should check out this one about the best London coworking space.
We also wrote about a few related subjects like Angel investors UK, tech companies in London, EMI scheme and Venture capital firms in London.
- 35 Successful Startups You Could Learn From - January 18, 2024
- The Biggest IT Outsourcing Failures: 7 Examples - January 14, 2024
- Famous Business Pivot Examples That You Should Know Of - January 13, 2024