The 21st century has seen the development of the Internet. It also witnessed the advent of platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter.
Search engines such as Google have changed the world of information. Many people have access to a smartphone with limitless information within easy reach.
Almost anyone can run a Facebook or Google ad campaign. This generates a highly competitive environment.
In this context, it is hard to stand out among competing companies. This is an ever-growing challenge for advertisers and marketing experts.
Today’s advertising companies have to find new ways to reach their targeted niche. Luckily, they were able to find an interesting solution: individual ad targeting.
This has been the standard method for digital advertising since the mid-2000s. It works based on web cookies.
Yet, as years pass, the use of cookies is being limited. Users can delete cookies or install an ad blocker on their web browsers.
Also, there are new privacy laws such as GDPR and CRPA. Marketing professionals can no longer rely on cookies like they used to.
So, advertising companies needed a new way to track customers’ behavior across the web. Hence the creation of device fingerprinting.
What is device fingerprinting?
Device fingerprinting works in the same way as with people. A person’s fingerprints are unique and can identify their identity.
It is possible to do the same with devices.
Device fingerprinting allows the collection and storage of a person’s information through their devices. It is also known as canvas, browser, and machine fingerprinting.
There is a key difference between the use of cookies and mobile device fingerprinting. While the former stores the data on the user’s side, the latter stores it on a server’s database.
The device fingerprint is created by analyzing different characteristics of a mobile device. These include IP address, browser version, language settings, operating system.
The unique combination of these factors establishes a unique device ID. With this ID, any entity can create a profile of the mobile device and the owner and track it across the web.
Cookies are usually stored in the user’s browser and users can delete them at any time.
However, device fingerprints can remain stored by the server. They are also used to track a person’s behavior.
Device fingerprinting relies on the probability that a mobile device with certain characteristics is the same one that appears on other occasions with the same characteristics.
The information advertisers use to create a device fingerprint
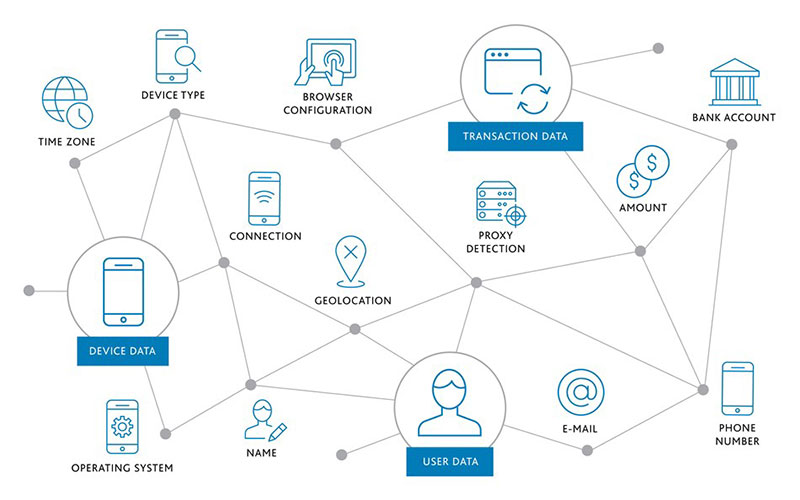
The process of mobile device fingerprinting relies on data collection. This can be:
- language settings
- hardware
- screen resolution
- installed plugins
- color depth
- operating system
- time zone
- browser versions
- browser extensions
They also track whether the device has the “do not track” function enabled. Although nobody respects this.
The following data is often used for browser fingerprinting:
- Timestamp
- IP address
- List of mime-types
- HTTP request headers
- Silverlight data
- User-agent string
- Plugins
- Installed fonts
- Time zone
- Flash data provided by a Flash plugin
- Operating system
- Device language settings
- Screen resolution
We can help you turn your idea into reality, take over your existing project, or extend your current development team.
Schedule a free consultation at hello@tms-outsource.com, or fill out the form and we will follow up with you shortly.
The uses of device fingerprinting
Mobile device fingerprinting was firstly used to prevent piracy and deceit.
Anti-fraud companies use this resource to prevent credit card fraud. They also identify devices that have involvement in fraudulent transactions.
Now, device fingerprinting is for online tracking. It is possible to identify a person by tracking their activity on multiple devices.
For this reason, it has become a valuable tool for advertising companies. They can use this information to target potential customers.
By using web cookies and device fingerprints, marketers can design more effective ads. Thus they can reach those people who are most likely to buy their products or services.
The following are some examples of how to use mobile device fingerprinting.
Tracking and analytics

Device fingerprinting has one very common use. This is to analyze results and track an ad campaign’s performance.
It is also an excellent tool to track users and understand a website’s audience. For example, to track new and returning visitors.
Fraud prevention
Device fingerprints help to prevent and identify bank or credit card fraud. Device IDs are unique, so it is possible to identify a device involved in a deceitful transaction.
A transaction made from the same device can be tracked even if they use a fake IP address, a proxy, or a different credit card.
Identify e-commerce fraud
Device fingerprinting is useful for e-commerce owners. Thanks to this tool they can identify an order placed by a swindler and cancel it if necessary.
Device fingerprinting use in AdTech
People use the internet for all sorts of things. For shopping, research, entertainment, and other online services.
For this purpose, they use different devices. This creates a challenge for brands that need to connect with potential customers.
Higher privacy protection supported by new regulations makes tracking a more challenging endeavor.
From the 2000s and on, data collection for advertising purposes occurred through cookies. But these have limitations.
Cookies can be blocked or deleted. But a device fingerprint is much harder to remove.
Thus, advertising companies prefer to use device fingerprinting.
Moreover, this technique is more effective than cookies. It provides an accurate profile for online users.
Advantages of device fingerprinting over cookies
Disadvantages of cookies for tracking purposes:
- Cookies make ads more recognizable. It’s possible to block ads with blocker software.
- Cookies can be easily removed by users.
- Cookies don’t provide a reliable way to track actions through mobile devices.
Why use device fingerprinting? – 4 reasons
- Device IDs form the basis of tracking ads. However, this method does not track the overall performance of a marketing strategy.
- Many advertising companies cannot support the integration of advertising identifiers. Hence, it is difficult to track the success rate of an ad.
They cannot determine who the user is and if they placed an order from the ad.
- People are online most of the time performing different activities through multiple devices. Thus, it is difficult for brands to connect with current and prospective customers.
- Due to increasing privacy regulations, people are deleting cookies and installing ad blockers. This makes cookies less effective and can negatively affect a business’s ROI.
If cookies don’t provide the desired results, an advertising company can use device fingerprinting.
This technology tracks the unique device ID and identifies the customer. This makes advertising much more effective.
Device fingerprinting: How does it work?
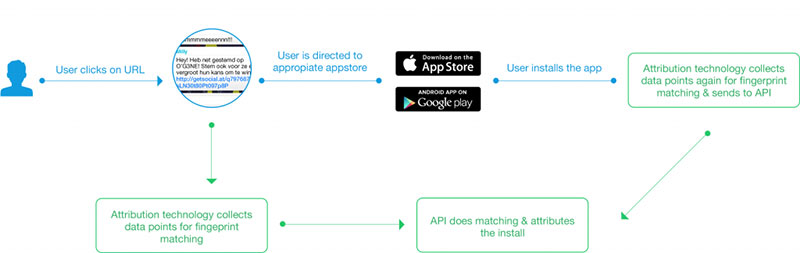
The information to create a browser fingerprint is collected online. When a user logs in to a site, a special tracker collects all the device’s information.
When someone enters a website, there are a variety of elements such as HTTP headers or Javascript. These can track the device’s characteristics (operating system, font system, etc.).
This helps to show results according to the device’s screen resolution, language settings, and location.
Javascript scans these attributes. It uses them to adjust the page format, to decide which languages to show and which products to display.
If accessed through a mobile app, the site will show its version for smartphones. If accessed from LA, the site will show the products that are closest to your location.
Browsers act like “user agents”. This means they act on behalf of the user, i.e., the person who is visiting the site.
The browser “reads” the characteristics of the device and uploads the corresponding site. Web developers use this data to provide visitors with a better user experience.
Every browser has a unique agent user string. This helps the server understand which browser is trying to upload content.
This is the basic principle of device fingerprinting. After this, the process is like a game.
The more information a browser gathers on a device, the better the advertisers can create a person’s profile. Then it becomes easier for them to target people with the correct product.
Running a device fingerprint system requires large storage space. This is because it stores the information server-side.
Unlike cookies, device fingerprints are not distributed back to the browser.
This technology offers companies an incredible advantage. It is almost impossible to prevent device fingerprinting.
Many websites use a form of device fingerprinting without the owner even knowing it. If it has Google Analytics installed, the tracking system analyzes where visitors are coming from.
This tool helps to understand which devices visitors use, their location, and more. This is valuable data that a website owner can analyze and use for their business strategy.
FAQs about device fingerprinting
1. What is device fingerprinting and how does it work?
Device fingerprinting is a technique for tracing devices that involve gathering information about their distinctive characteristics, such as the type of browser being used, the screen resolution, and the installed typefaces. When all of this data is integrated, a distinctive “fingerprint” that may be used to recognize the device is produced. This information is gathered through a user’s browser and stored on a server as part of the device fingerprinting process.
2. How accurate is device fingerprinting in identifying devices?
Device fingerprinting has a high accuracy rate for identifying devices, frequently over 90%. This is because it is challenging for two devices to have the exact same fingerprint because the set of data points needed to build a device fingerprint is highly unique.
3. Can device fingerprinting be used to track user activity across multiple devices?
Device fingerprinting is normally used to monitor behavior on a single device, but if users use the same browser or have the same loaded fonts and plugins on numerous devices, it may also be used to monitor activity on those devices.
4. What are the potential privacy concerns with device fingerprinting?
Device fingerprinting raises privacy and user control issues because it can be used to track users without their knowledge or consent. Also, it can be used to gather private data about users, including their location, device type, and browsing preferences.
5. How can users protect themselves from being fingerprinted?
By adopting privacy-focused browsers or browser plugins that restrict or obfuscate device fingerprinting methods, users can guard against being fingerprinted. Additionally, they can restrict or deactivate the use of plugins and cookies, as well as hide their IP address and location using virtual private networks (VPNs) such as AstrillVPN or Tor.
6. Can device fingerprinting be used for authentication and security purposes?
Indeed, device fingerprinting may be applied to security and authentication. It can be used, for instance, to spot fraudulent or dubious activities, including account takeovers or bot attacks. On the basis of specific device characteristics, it can also be used to authenticate people.
7. Are there any legal regulations around device fingerprinting?
Device fingerprinting is not yet subject to any specific legal requirements, however depending on how it is used and the type of data collected, it might be covered by general data protection rules, including the GDPR and CCPA.
8. How does device fingerprinting differ from traditional tracking methods such as cookies?
Device fingerprinting is different from conventional tracking techniques like cookies in that it gathers a far wider variety of data points and may still be used to identify devices even after cookies are disabled or removed. Due to its reliance on hard to alter or spoof data, it is also more challenging to identify and block.
9. Can device fingerprinting be used to identify a user’s location or geographic region?
Indeed, a user’s location or area can be determined via device fingerprinting based on their IP address, language preferences, and other device characteristics. Based on a user’s location, this information may be used to target ads or alter the content.
10. How can website owners use device fingerprinting to improve their website’s user experience?
The content and user experience of a website can be customized based on a user’s device through device fingerprinting, a technique used by website owners. For instance, they might recommend products based on a user’s installed plugins or browsing history, or they might optimize the layout for a particular screen resolution. The owners of websites should provide users access to their data and be open about how they employ device fingerprinting.
Ending thoughts on device fingerprinting
As time goes by, technology evolves. The digital advertising industry is becoming more challenging and complex.
Advertisers and marketers are dealing with a market formed of different generations. People who grew up with a black-and-white TV and children who were born with a tablet in their hands.
The new technologies and gadgets are challenging every person on earth. Especially those who profit through online services.
Users are becoming more unpredictable and tracking more complicated. Advertisers find a solution to these challenges thanks to device fingerprinting.
They can fill the gaps in their marketing strategies. As a result, they boost their business and increase revenue.
This system works by gathering the device’s data instead of the user’s. This means that privacy laws are not violated.
The GDPR lists some information gathered by device fingerprinting as personal data. It is advisable to consider this when implementing such a strategy.
If a marketer wants to target a person, and not a device, then using cookies is the only solution. But this strategy has limitations and it may generate privacy issues.
If the online advertising industry can follow Google’s lead in creating a more transparent cookie system, then this might be the best approach. It would offer a good solution both for companies and internet users.
In conclusion, device fingerprinting is a great alternative for advertising strategies. It allows for the collection of a device’s data.
It also offers the advantage of storing this information on a server’s database. When using this strategy, it is important to consider the legislation that protects users’ privacy.
If you enjoyed reading this article about device fingerprinting, you should check out this one about what is AdTech.
We also wrote about a few related subjects like behavioral targeting, MVP tests, personalization algorithms, how to hire a web development team, software development budget, financial projections for startups, financial software development companies, proof of concept vs prototype, and MadTech.
- 35 Successful Startups You Could Learn From - January 18, 2024
- The Biggest IT Outsourcing Failures: 7 Examples - January 14, 2024
- Famous Business Pivot Examples That You Should Know Of - January 13, 2024