Imagine whipping up an app as easily as your favorite weekend pancake recipe. That’s right—no hefty price tags, just you turning your brainchild into a clickable, touchable reality on screens worldwide. Welcome to the game-changing universe of open-source mobile app development software.
Here, it’s not just about writing code; it’s about weaving connections between your ideas and the pixels dancing on our devices. This isn’t just any article. You’re about to embark on a digital DIY adventure, unlocking the secrets to transforming that app vision bouncing in your head into a living, breathing reality—without the need for a Scrooge McDuck-sized bank vault.
By the end of our chat, you’ll be savvy on all things open-source for mobile apps—from fluttering through Flutter, reacting with React Native, to syncing with Xamarin.
Ready to be that person? The one who says, “Yeah, I made that app”? Stick around.
Top Open-Source Mobile App Development Software
| Mobile App Development Software | Open-source | Platform Support | Programming Language(s) | Main Features / Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flutter | Yes | iOS, Android, web, desktop | Dart | High-performance apps with customizable UI & “hot reload” for rapid development. |
| Xamarin | Partial | iOS, Android, Windows | C#, .NET (Xamarin.Forms) | Shared code across platforms with native performance. Strong corporate backing (Microsoft). |
| Mobincube | No | iOS, Android, web | Visual drag-and-drop | No-code platform focused on building apps without programming skills. |
| Android Studio | No | Android | Java, Kotlin | Official IDE for Android development with advanced tools for profiling, debugging, etc. |
| Ionic | Yes | iOS, Android, web | HTML, CSS, JavaScript | Build cross-platform apps with a single codebase using web technologies. |
| Sencha Ext JS | No | iOS, Android, web | JavaScript | Create data-intensive cross-platform web and mobile applications. |
| Alpha Anywhere | No | iOS, Android, web | JavaScript, Xbasic | Rapid development of business apps with a focus on offline capabilities. |
| Felgo | Yes (for personal use) | iOS, Android, desktop, embedded | QML, JavaScript | Develop cross-platform apps and games with less code; focuses on ease of use. |
| Buildfire | No | iOS, Android, web | JavaScript (with plugins) | Mostly no-code platform with customizable templates and a plugin marketplace. |
Some distinctions to keep in mind:
- Open-source: Platforms like Flutter and Ionic are open-source, while others like Xamarin offer open-source frameworks or components.
- Platform Support: Most of these tools support iOS and Android, with some extending to web, desktop, or even embedded systems.
- Programming Language(s): The language varies widely. Flutter uses Dart, Xamarin uses C# with .NET, and Ionic relies on web technologies. Others provide visual drag-and-drop environments or no-code solutions.
- Main Features: Some are focused on performance and native feel (Flutter, Xamarin), others on ease of use and no-code development (Mobincube, Buildfire), and some on web technologies (Ionic, Sencha Ext JS).
Flutter
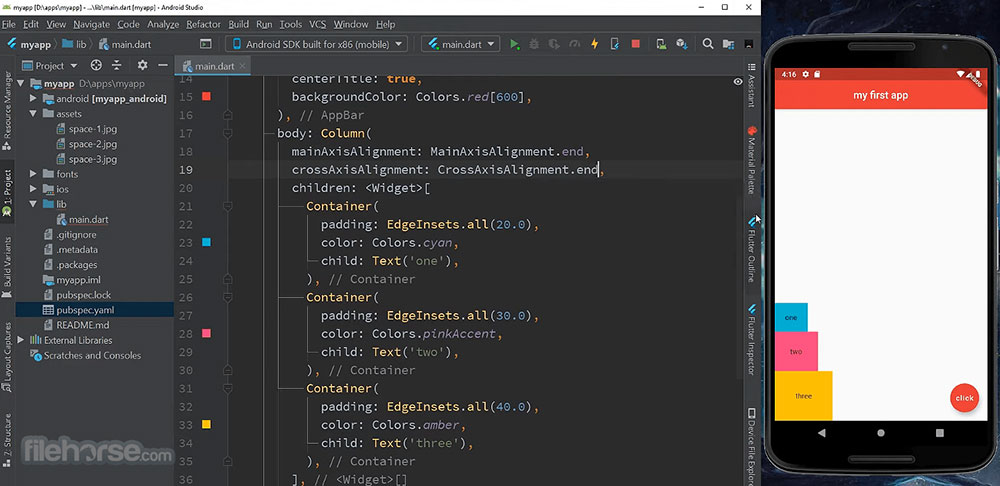
Flutter is like a magic wand for app creators. It’s the paint and canvas for your digital masterpieces, letting you craft nifty, natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase. Flutter’s hot reload feature feels like having a time machine, making tweaks and seeing them instantly – pure magic.
Best features:
- Single codebase for all platforms
- Rich set of fully customizable widgets
- Hot reload for instant updates
Xamarin
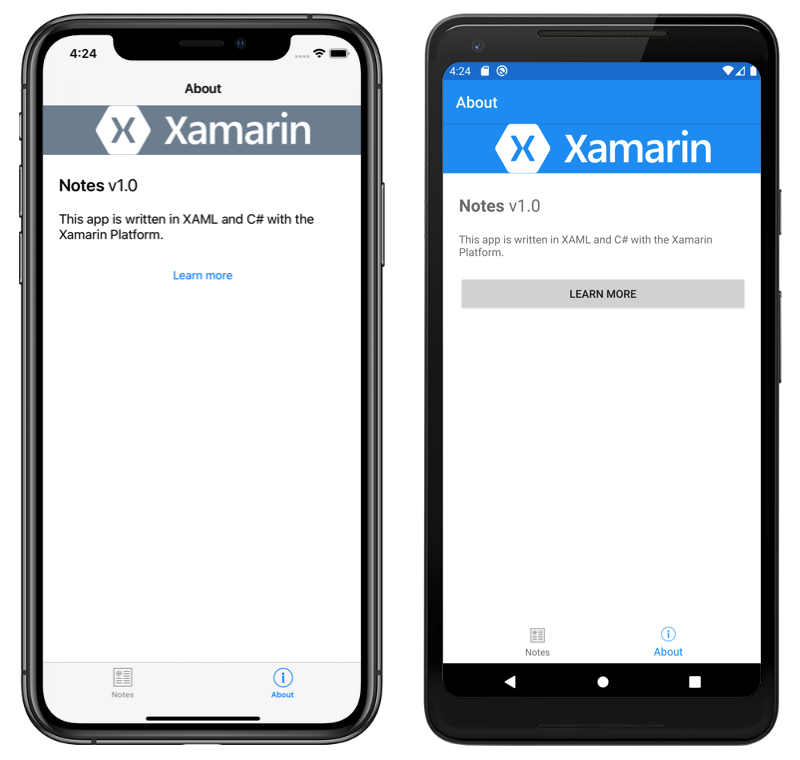
Xamarin’s the trusty sidekick for developers who love C# and .NET. It feels like having a universal key, unlocking doors to iOS, Android, and Windows apps with just one robust language. Sharing code across platforms? Xamarin makes it a breeze, and native performance is just the cherry on top.
Best features:
- Native performance
- Shared codebase for multiple platforms
- Strong community and Microsoft support
Mobincube
Mobincube marches to the beat of a different drum, with its no-code approach that’s as sweet as a pie for non-coders. Imagine sliding blocks into place and presto, you’ve got a functional app. It’s a haven for those who want to build without the headache of heavy coding.
Best features:
- Drag-and-drop interface
- No coding skills required
- Monetization options
Android Studio
Android Studio is like having a Swiss Army knife in your pocket, but for Android app development. It’s built by Google, so you’re tapping into some top-notch tools. With a build system that keeps things running smooth and a suite of emulators, it’s a lifeline for Android-specific craftsmanship.
Best features:
- Integrated Android emulator
- Powerful code editor with advanced features
- Visual layout editor
Ionic
Ionic is like a bridge connecting web developers to the land of mobile apps. Using familiar web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, it’s like getting VIP backstage access to both Android and iOS platforms, all without leaving your web comfort zone.
Best features:
- Use of web technologies
- A vast library of plugins
- Strong community support
Sencha Ext JS
Sencha Ext JS is like the blueprint for building data-intensive cross-platform web and mobile applications. Imagine creating intricate applications that behave like those snazzy desktop ones, making it a solid pick for enterprises craving sophisticated interfaces and top-notch performance.
Best features:
- Data-driven components
- Rich UI widgets
- Robust data package
Alpha Anywhere

Alpha Anywhere is like a trusted guide through the jungles of business app development. You’re equipped with a set of tools that make it simple to build powerful web and mobile apps that handle massive data, all with some neat offline capabilities for the path less traveled.
Best features:
- Offline access
- Data integration and synchronization
- Rapid development capabilities
Felgo
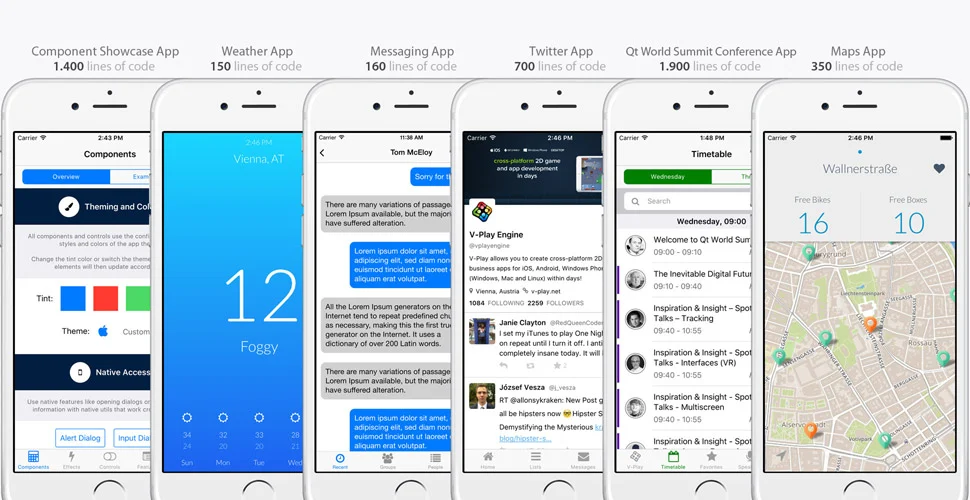
Felgo is like your personal GPS for app creation, helping you navigate through the development process with ease. It uses the power of QML and Qt, allowing for speedy development and prototyping. In the world of Felgo, crafting apps for multiple platforms is as easy as pie.
Best features:
- Hot reload for rapid prototyping
- Native performance across multiple platforms
- Easy integration of plugins and services
Buildfire
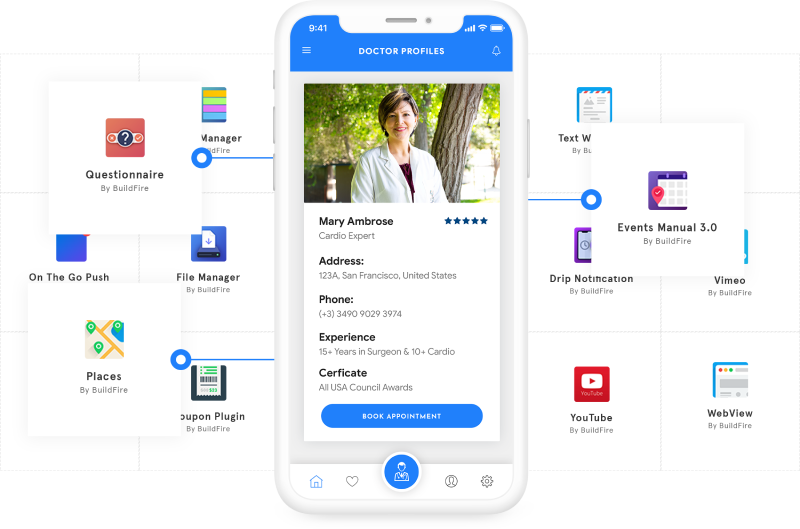
Buildfire is like your friendly neighborhood tool-shop, offering a wealth of plugins and a mere “point-and-click” approach for building apps. With features galore and a supportive community, Buildfire empowers you to construct shiny apps even if you’re new to the block.
Best features:
- Intuitive app builder with drag-and-drop simplicity
- A rich marketplace of plugins
- Customizable templates and design options
FAQ on Open-Source Mobile Development Software
What exactly is open-source mobile app development software?
It’s the toolkit for the digital tinkerers. Open-source mobile app development software is like a communal shed, stocked with tools that anyone can use, modify, and share to create mobile apps. From React Native to Flutter, they’re revolutionizing how we craft code without the cash crunch.
How do open-source frameworks like Flutter and React Native compare?
They’re like two different spices in a coder’s kitchen. Flutter is all about the Dart language, offering that smooth, one-codebase fits all platforms vibe. React Native? It’s JavaScript’s best friend, giving you that ‘write once, run anywhere’ magic. Both spice up the coding life, just depends on your taste.
Can I build an app for both Android and iOS using these platforms?
Absolutely! That’s the sweet spot of these open-source heroes. With just one set of code, boom, you have an app that’s friendly with both Android and iOS. Thanks to the cross-platform capabilities, you’re like a bilingual diplomat, breaking down the barriers between the app worlds.
Are there any hidden costs with using open-source software for app development?
Well, the supermarket’s open and the software’s on the house. But sometimes, you might want to grab a shopping trolley for a smoother ride. That’s stuff like added features, support, or integrations. They might require a little extra dough, but for the basics? Your wallet stays closed.
How do I get support for open-source app development tools?
Think of it like a potluck; everyone brings something to the table. Online communities, forums, Stack Overflow—it’s a smorgasbord of tips, tricks, and help. Plus, there’s documentation for days. Need something more? Some frameworks offer paid support if you need that VIP treatment.
Is it secure to use open-source mobile app development frameworks?
Imagine a castle with an open-door policy. Sure, everyone can come in, but it’s the collective of good knights—developers and security experts—that keep the place safe. These folks are always patching up holes and building better walls. It’s commUNITY strength that keeps your digital fortress secure.
Do I retain intellectual property rights when using open-source software?
Owning your creation? It’s a yes! The canvas is theirs, but the art? All yours. Open-source licenses like MIT or GNU GPL are like a handshake agreement—they let you hold the reins to your masterpiece. Just make sure to nod to the software’s license terms.
Can open-source tools keep up with the fast-paced mobile market?
Think of these tools as the nimbleness of a street performer, quick to adapt to the beat of the city—or in this case, the tech rhythm. Frequent updates and passionate communities have you covered, hands down. These frameworks move fast, grooving with the perpetual dance of progress.
How does the performance of open-source apps compare to proprietary ones?
Here’s the deal, it’s not about who’s wearing the fancier suit. Open-source apps can tango toe-to-toe with proprietary ones. Performance? Snappy. Features? Rich. The catch? It’s down to the maestro—yep, that’s you—the developer’s skill, ensuring your app hits that high note.
What is the future of open-source app development?
It’s like peering into a crystal ball, and seeing a whole park of folks flying their DIY drones. The future? It’s community-driven, boundary-pushing, and bright as ever. Open-source is not a passing cloud—it’s here, brewing like a storm, ready to rain down innovation for years to come.
Conclusion
Diving into the world of open-source mobile app development software is like exploring a new city with an all-access pass. You’ve seen the sights, from the towering frameworks of Flutter and React Native to the bustling marketplaces of GitHub and GitLab. It’s a place where the only limit is how far your creativity can stretch.
- Imagine your app ideas taking flight, no strings attached, no price tag looming.
- Envision a community where sharing beats competing, and everyone has a seat at the table.
- Picture troubleshooting with a global team where someone, somewhere, has the answer you need.
Wrapping up, we’ve walked the streets of open-source together, seen the artistry in coding for platforms like Android and iOS, and realized that this isn’t just programming—it’s digital craftsmanship. Carry this knowledge, the know-how you’ve gained, and the tools you’ve discovered. Your next creation awaits, and the code is your canvas.
If you enjoyed reading this article on open-source mobile app development, you should check out this one about the top IDE for web development.
We also wrote about a few related subjects like the best IDE for Flutter, Java, C++, Javascript, and for Mac.
And we managed to create comparative articles like Sublime Text vs Notepad++, Sublime Text vs PyCharm, and VScode vs Sublime Text.
- Ultimate Streaming: Entertainment Apps Like Kodi - April 19, 2024
- Design’s Descent: What Happened to Fab? - April 19, 2024
- Design Basics: iPhone App Icon Size Requirements - April 19, 2024