The marketers’ world has changed forever with the advent of personalization algorithms.
Traditional methods took a broad approach. Companies would advertise their best products or services. Then they would hope. Maybe it reached their target audience, maybe it wouldn’t.
Machine learning and other AI tools for business have changed all that and there’s no going back. Internet users now expect to see relevant content tailored specifically to them.
Personalization is the new way to market to potential customers. This process relies on data scientists and artificial intelligence.
The algorithm collects customer behavior data. Then it uses those data sets to offer a customized experience. The learning algorithm then creates messages, promotions, and advertisements that are users based.
This means improved conversion rates and an improved user experience.
These marketing algorithms are used in most companies’ advertising efforts. Still, there are many who are unfamiliar with the details. What exactly is an algorithm? What do they do? How are they utilized in today’s marketing efforts?
This article is here to make you an expert on personalization algorithms.
It’s All About Algorithms
Machine learning personalization is based on various factors. Analytics, filters, and algorithms all come together to understand users.
Their behavior, preferences, methods, and more are compiled into data points. An algorithm takes those data points, or other kinds of input, and uses them to create an output.
This is similar to the way numbers in a math formula are inputted into a calculator to produce the answer.
Algorithms are what power artificial intelligence (AI) for machine learning.
Similar to humans, an AI can be exposed repeatedly to large amounts of data and taught. Eventually, it can come to understand what the data means. Then make meaningful predictions based on what it’s learned.
An AI’s algorithms enable it to offer relevant content recommendations to customers, often in real-time.
Algorithms are what makes Google so successful. When we search for a topic, an algorithm is used to determine the best possible result. Another algorithm’s analysis will find us a matching service or product. Then we are given the result in a Facebook ad the next time we log in.
When we buy a baking pan on Amazon, we could be sent an email advertising the perfect spatula to go with it. An algorithm examined the habits of thousands of customers. Then it chooses that specific spatula for us.
These are just two simple examples. Algorithms are the key ingredient in the personalization strategy of marketing. So there are many other applications. Algorithms equip marketers from a variety of fields to provide personalized content.
How Algorithms Can Work For You
Algorithms can be used to make your website visitors stay longer. They can make sure your visitors see specific things and encourage them to return. To do that, it needs to gather the right data.
There is a near unlimited amount of data that can be collected. You’ll want to choose and configure algorithms that best align with your website’s needs.
They can determine what content, service, or product to suggest to your site’s visitors. So a good place to begin is with simple recommendation algorithms.
For example, the right algorithm can collect the general trends of your users. What is the most frequently viewed page within your website during what specific times? What sort of purchase history does each user have?
This data will inform what specific kinds of advertisements would be best. It also helps you to know when and where to deploy them.
E-commerce, digital advertising, and media companies rely on personalizing the customer experience. The ability to provide hyper-personalization affects their performance. This hyper-personalization can take the form of:
- Relevant content suggestions
- product recommendations
- Advertisements
- Customized responses
If one user tells you their opinion of an item that means they share something in common with other visitors. An algorithm can make recommendations based on the user group’s behaviors.
If many people in this group bought a particular product, chances are good that other members will too.
Let’s take a look at another example – creating dynamic content based on a set of conditions or triggers will allow you to show them products relevant to their data such as location, user behavior, pages visited, etc.
These models rely on artificial intelligence. The AI creates a real-time propensity score for each user according to the chance each will follow a pre-set action.
This is called predictive targeting.
The machine learning software examines the data from all visitors to its websites. It then finds similarities. Eventually, the data it gathers allows it to predict the actions of each visitor.
Collecting Visitor Data and Learning
Imagine an AI playing a chess game. It knows the best move because it has studied tens of thousands of individual chess matches.
The same is true for a marketing algorithm. It takes a complicated set of metrics and compares them to similar metrics from the past. Based on that comparison, it gives a recommendation.
Every time a user does anything on your site, you learn new things. Customers leave information about their preferences when they use search engines or social media. Even when they visit stores they leave behind clues.
Their behavior can be understood and predicted from data like:
- Site Navigation Paths
- View Durations
- Search Refinements
- Back-and-Forth Navigations
The more of these you manage to collect, the more accurate your customer predictions will be. This means your company can more easily and accurately access their needs.
When you display content that is personally relevant to each user, you make them feel welcome. This in turn guides them to conversion.
You will thoroughly learn practical data about your clients, such as:
- What stage of the buyer’s journey they’re in
- What methods they use to shop
- What they enjoy doing
- How likely are they to make major financial choices
- What they’re capable of and likely to invest in
Examples of Predictive Content Personalization
Almost every industry is creating projects that use personalization. Since it happens behind the scenes, most customers may not be aware it even exists.
Here are some familiar examples:
Netflix
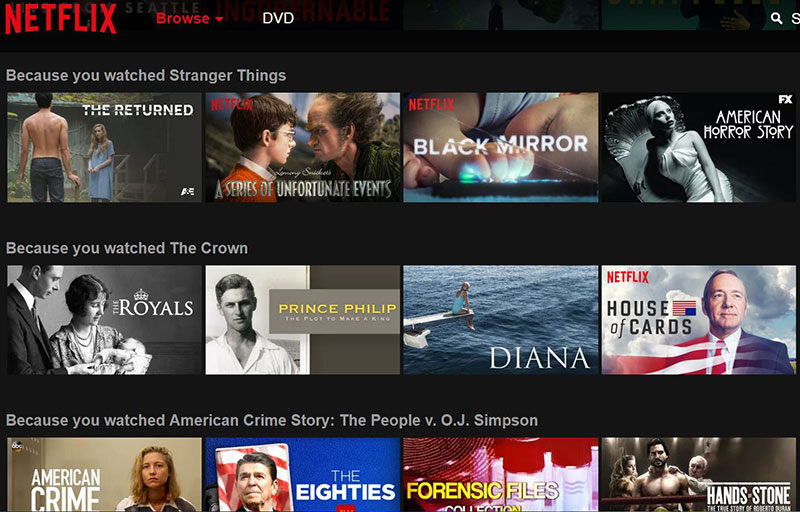
Netflix has more than 57 million users worldwide. It would be impossible to create a single homepage to fit their collective interest.
Instead, it employs a complex set of algorithms that determine each individual’s preferences. Then it fills their personal homepage with movies and TV shows just right for them.
Thread
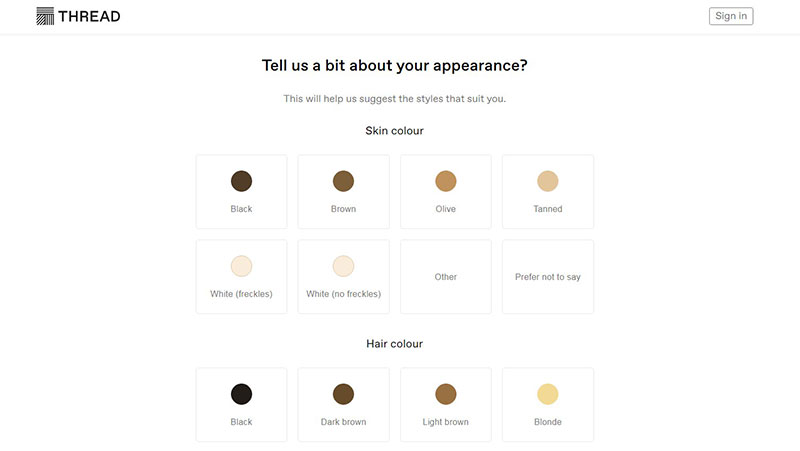
Clothing is a very personal expression of style. No one company can be relied on to define every individual’s style, but Thread comes close.
It uses AI to remember what each customer likes. Then it uses that pattern to personally suggest clothing options.
The more data they collect, the closer the suggestions come to being accepted.
Spotify
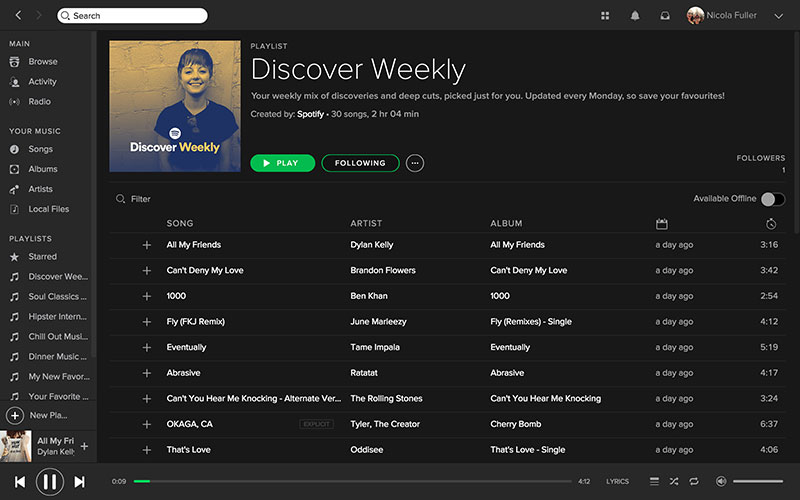
Gone are the days when we relied on friends for personally curated musical knowledge. Spotify’s model uses an AI that uses a listener’s previous music habits to predict what music they enjoy.
Then it presents those suggestions in an array of playlists. Release Radar, Discovery Weekly, and Spotify Radio are all personalized for each customer.
Amazon
The available stores and products on Amazon are nearly limitless. To account for every possible shopper with one home page would be impossible to achieve.
Instead, it changes the front page to match each individual shopper. What is recommended to you will not be the same as what is recommended to someone else.
But it doesn’t stop at the storefront. They also use the same practice to display promotions to customers who have made previous purchases before.
Data Crunching
The data science behind this method is only possible because of two things:
- The scope of data collected
- The meaning found from the data
You may think broad data like user demographics and location is most important. To really succeed though, the data collected needs more information than that.
Behavioral data is what really gives context. It makes an algorithm precise and effective.
As this technology continues to advance, it is becoming more rooted in marketing practices. The level of automation will develop right along with it.
The many algorithms can record:
- Brand preferences
- Product usage
- Posts and comments on social media
- Websites frequented
They can even use one individual’s data to interpret another individual’s data.
The most advanced AI can even present a higher level of personalization through dynamic content. These programs are not limited to recommendations. They can modify entire web pages or page modules to match each user.
This means that some users can be taken to entirely different landing pages than others.
This customized approach is valuable for the benefits it brings both the customers and the company. It streamlines the experience for each customer and increases the likelihood of sales for the company.
FAQs about personalization algorithms
1. What is a personalization algorithm?
A particular kind of machine learning algorithm called a personalization algorithm examines user behavior, preferences, and other information to produce a tailored experience for every user. Personalized recommendations, information, and services are offered to users in a range of industries, including e-commerce, social networking, and healthcare.
2. How do personalization algorithms work?
Personalization algorithms gather and examine user information, such as browsing patterns, search terms, and purchase histories. Based on this information, the algorithm develops a user profile and suggests products or content that are pertinent to the user’s tastes and interests.
3. What kind of data do personalization algorithms use?
Several data sources are used by personalization algorithms, such as user demographics, browsing and search histories, purchase histories, geographical information, and social media activity. The kind of data used varies depending on the sector and how the algorithm is applied.
4. What are the benefits of using a personalization algorithm?
Increased user engagement, better customer happiness, higher conversion rates, and higher income for organizations are all advantages of implementing a customization algorithm. Users who might not have otherwise found new products and information can benefit from personalization algorithms.
5. How do personalization algorithms impact privacy?
By gathering and examining user data, including potentially sensitive information like location, browser history, and social media activity, personalization algorithms can have an influence on privacy. Businesses need to be honest about their data collection and usage practices since users could be worried about how their data is used and shared.
6. How do personalization algorithms differ from recommendation algorithms?
Both recommendation algorithms and personalization algorithms employ machine learning to give users individualized content and product recommendations. While recommendation algorithms make recommendations based on larger patterns and trends, personalization algorithms take into consideration specific user preferences and behavior.
7. Can personalization algorithms be biased?
Indeed, personalization algorithms may be biased if they were developed using biased data or if their own assumptions or reasoning were skewed. To guarantee that all users are treated fairly and equally, it is crucial for organizations to keep an eye on and eliminate biases in their personalization algorithms.
8. What are some examples of successful personalization algorithms in different industries?
Amazon’s recommendation engine, Netflix’s individualized content suggestions, and Spotify’s personalized music recommendations are a few instances of successful customization algorithms. Personalization algorithms are used in healthcare to offer individualized treatment regimens and forecast health outcomes based on specific patient data.
9. How do businesses decide which personalization algorithm to use?
Companies may assess various personalization algorithms depending on the kind and amount of data they gather, the algorithm’s complexity, the reliability of the recommendations, and the price and scalability of the solution. Companies can experiment with and compare several algorithms to see which produces the best outcomes for a given application.
10. What are some common challenges associated with implementing a personalization algorithm?
Large-scale data collection and processing, data privacy and security, overcoming algorithmic biases, and integrating the algorithm with current systems and procedures are common issues involved with deploying a personalization algorithm. Personalization algorithms may also need a lot of time, money, and experience to create and maintain.
Ending thoughts on personalization algorithms
Customers want to be listened to. They will be attracted to the brands that pay attention.
Personalization is how your business can do just that.
It’s the best way to contextualize messages, promotions, and experiences to match every unique customer.
At this point, you’re well versed in the data science behind personalization algorithms. You’ve learned from the example of some of the best businesses that use it.
The key will be finding the balance between, “We think you might enjoy this” and “We’re always watching”.
Make sure to plan ahead well before taking the leap into any customization initiatives. This guide is a good start, but all our other articles will fully prepare you for all your algorithm needs.
If you enjoyed reading this article on personalization algorithms, you should check out this one about business pivot examples.
We also wrote about a few related subjects like how to hire a web development team, software development budget, financial projections for startups, financial software development companies, IT outsourcing failures, and software development outsourcing trends.
- What Are Third-Party Cookies and How They Work - April 20, 2024
- How Do Websites Detect Adblock? It’s Quite Simple, Actually - April 14, 2024
- Financial Software Development Companies You Should Know - April 11, 2024