Companies used to rely on traditional advertising campaigns to reach new customers. These days, behavioral targeting is a marketing strategy used by many companies to secure new and current customers.
Before the advent of behavioral targeting, it was hard to predict the success of an advertising campaign. Companies would create ads and marketing messages that failed for no apparent reason. This was due to marketers failing to display relevant ads that appealed to the interests of potential customers.
The development of web tracking technology made it possible to track the web browsing behavior of individual users. This resulted in the birth of behavioral targeting.
Behavioral targeting led to the use of personalized ads and behavioural messaging platform to connect better with prospects. This was done by pairing user contact data with real-time info about the online behavioral data of individual users on websites and apps.
This article will define behavioral targeting, discuss its benefits, and explain how it works.
What Is Behavioral Targeting?
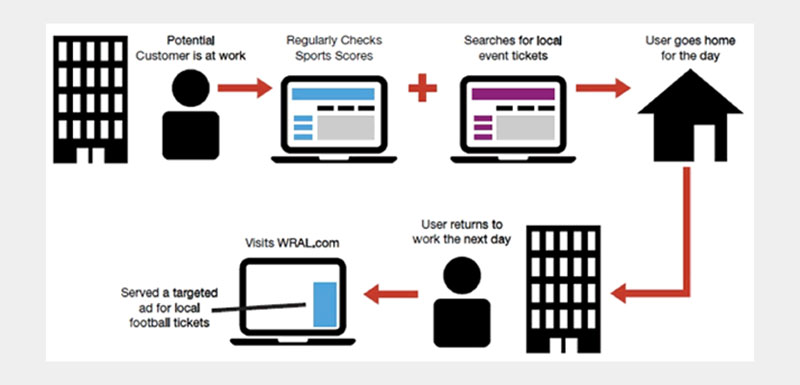
The behavioral targeting process utilizes third-party cookies and tracking pixels. It involves displaying relevant content based on a customer’s online footprint. This means that the type of marketing messages a customer sees depends on their internet activity.
Behavioral targeting makes online advertising a flexible process. For example, two visitors may be using a particular site, yet they both are shown completely different ads. This is because behavioral targeting operates based on an individual’s behavioral data. Such data may include:
- What users are doing in an app or website
- What users are not doing in an app or website
- How users interact with ad campaigns on various web pages, etc.
This is the kind of behavioral data that is at the heart of personalized marketing. This type of data hints at a user’s purchase intent and helps to drive engagement. Such data helps you to speak directly to prospects that are more likely to want your goods and services.
Essentially, behavioral advertising depends on the user’s online behaviors, such as:
Most-Visited Web Pages
A users’ interests may be discerned by knowing what websites they return to the most.
Page Dwell Times
The time spent on a particular site is a good indication of how absorbed the user is with the site content.
Ad and Link Clicks
The ads and links users click are good indicators that they may be interested in similar topics or products. Such behavioral tracking enables advertisers to leverage targeted ads.
Web Search Queries
Collecting information about what users search for online can reveal much about their purchase intent. User search behavior-tracking gets your goods and services in front of potential customers.
Especially in the late stages of the marketing funnel. For example, If a user googles a solution to a problem and your product is a good fit, your marketing message will be displayed.
Website Interactions
It’s important to harvest data about which types of content on your platform fosters higher engagement.
Do your users interact more with videos vs the other data content of your site or app? Or, maybe they like to listen to podcasts? Rich media, perhaps? Tracking user to platform interactions will tell you how to approach website personalization.
Purchase Histories
Tracking a user’s purchase history is a great way to generate leads. This is because knowing what a customer previously bought is a good way to identify their interests. This is particularly beneficial for E-commerce companies. So, it should be no surprise why so many eCommerce platforms with multiple vendors track a user’s purchase as it allows them to gain valuable customer data.
With behavioral targeting, marketers have access to a wealth of consumer data. This data is used to drive traffic via personalized ads and an improved user experience.
Behavioral targeting empowers publishers and advertisers to create new business in multiple ways, including running an Amazon PPC Campaign. For example, a customer searches Amazon for mobile devices but does not make a purchase.
When this customer visits other websites, Amazon’s advertising network will show ads for mobile devices. This increases the likelihood of the customer taking the desired action.
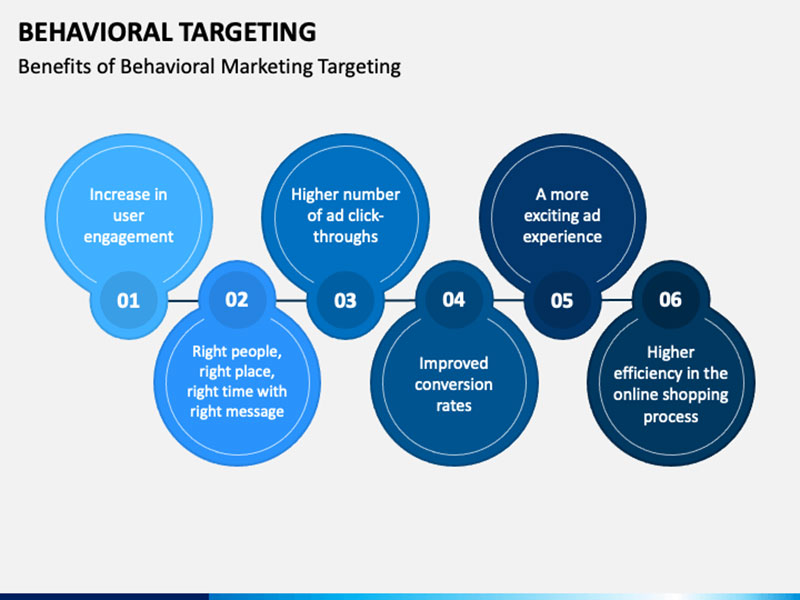
What Are the Benefits of Behavioral Marketing?
Before behavioral targeting, digital advertisers relied solely on contextual targeting. This is where customers would see ads related to the keywords and topic of a site. For instance, a kitchen knife ad on a cooking website.
Contextual targeting is still useful. But, successful behavioral targeting is much more powerful. It boosts the user experience of a website or app, which adds to customer loyalty.
Behavioral targeting may be data-focused, but it’s better than the abstract number systems used in some industries. Focusing a campaign on targeting behavioral patterns, benefits the customer and the advertiser.
Here are a few of the benefits of behavioral advertising.
Customer Re-Engagement
Behavioral targeting helps companies to reconnect with visitors that have abandoned their site. This is called re-engagement.
Behavioral targeting maps the user’s previous on-site interactions with products and services. To reinstate the relationship, personalized content is marketed to the user on different sites.
Personalized Advertising
Behavioral marketing makes for tailored or personalized advertising. This means companies can advertise to users based on their online activity. This increases the customer experience and the sales of the company.
Caution must be exercised to prevent ads from looking like an invasion of privacy, as this could hurt sales. For example, an ad that mentions a user’s wedding plans may appear overly personalized. This could make a customer feel like someone is collecting information they shouldn’t have.
Higher Number of Ad Click-Throughs
Behavioral targeting gets consumers to click on your ads by making them relevant. Personalized/ relevant ads capture the viewer’s attention much more than generic ads do. This helps to move them along the purchasing pipeline.
Initiate Long-lasting Communications
Behavioral targeting enables the engagement of specific segments of your audience. For instance, you may create newsletters for visitors from a specific country.
To gain their trust, let them take a look inside the newsletter and invite them to subscribe to the service. This approach initiates long-lasting communication with more consumers from your target audience.
Building Trust Through Retargeting
This involves the targeted advertising of goods repeatedly across various websites. This is based on the Rule of Seven marketing principle.
This principle states that prospective customers need to see a product ad 6-8 times before they buy. Such repeated exposure builds familiarity, familiarity builds trust, and trust drives conversions.
Bait Indecisive Prospects
Some consumers may indecisively browse through your site’s product offerings. Behavioral targeting helps to hook them via discounts, incentives, and personalized product offerings.
Improved Profits
Behavioral targeting results in higher profits, sales, and repeat customers for companies. Personalized recommendations increase the chance of consumers requesting more information about products. A good example of this is the growth of OTT platforms.
In the last few years, especially since the pandemic, there has been a rapid spike in the profits of all the major OTT platforms such as Netflix, Amazon, etc. This is because they used behavioral targeting (using the lockdown situation to their advantage) and increased their overall profits.
Improved Metrics for Advertisers
Behavioral targeting helps make ads more interesting, relevant, and personalized. This leads to greater consumer satisfaction, which in turn, increases the CTR, conversion rates, and the ROI of the advertiser.
Improved Ad Experiences
Consumers don’t like when companies have their personal data. But, when surveyed they indicate a dislike for generic ads. Behavioral targeting helps marketers build detailed profiles about users. This ensures only relevant emails and ads are forwarded to consumers.
More Efficient Online Shopping Process
When consumers see online product ads that suit their needs and click them, they are redirected to online storefronts. From there the item can be added to the cart with only a few simple clicks.
Increased Exposure To New Products
Behavioral targeting helps to promote new products. New products that relate to the consumer’s browsing history will be included in the personalized ads he/she sees.
The shopping experience is improved when consumers can get access to the latest versions of products at the right moment. This impacts the marketer’s profits, website traffic, and popularity.
How Behavioral Targeting Works
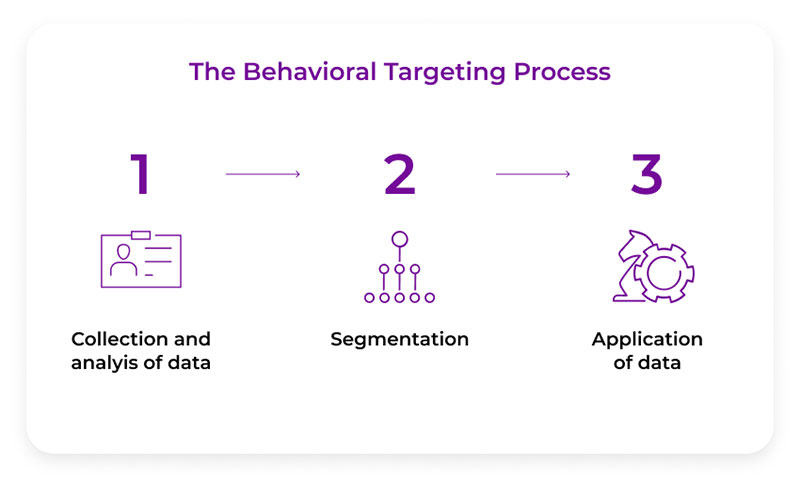
How does behavioral targeting work? The behavioral targeting process involves 4 steps to create a personalized ad experience. These include:
Collecting Consumer Data
- The first step in making behavioral targeting work is collecting consumer data. This can be done by collecting cookies about a user’s online patterns. Cookies are collected when a user visits a new site or sets up an online profile. Cookies are either stored temporarily on the user’s memory drive or permanently on their hard drive.
- Apart from data collected by DMPs and other AdTech platforms, data is also collected from registered user profiles. When registered users purchase from an online store, their purchase and site navigation history are stored by the vendor.
- A third way to collect and track consumer data is by Internet service providers (ISPs). These may perform deep packet inspections to identify the websites visited by registered users.
Creating Detailed Profiles
- Step 2 involves creating a big data/ personal profile for each user. These profiles include cookies and other data that map a consumer’s viewing history and online actions. This gives marketers insight into the user’s interests and shopping habits.
Segmentation
- Step 3 is about sorting users into categories based on their data profiles. Consumers may be segmented into groups like:
- Frequent travelers
- Antique lovers
- Shoppers who frequent a specific product category, etc.
This step enables websites to determine which ads to show different audience segments.
Application Of Collected Data
- At this stage, targeted advertising campaigns are developed and implemented. This is what causes relevant content to reach online users.
What Kind Of Consumer Data Are Data Management Platforms Allowed To Collect?
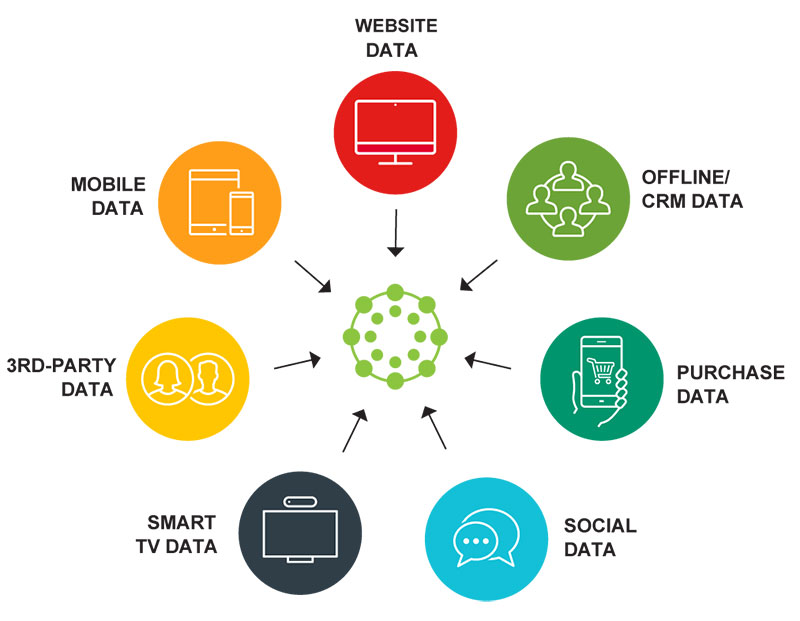
There are many sources from which consumer data can be collected. These include:
- Mobile apps
- Websites
- CRM systems, etc.
There are four types of consumer info that data management platforms can collect.
Website Cookie Data
This is data on how visitors interact with websites. A wealth of information can be collected as visitors spend time browsing a site. This includes:
- Pages visited
- Duration spent
- Country/ region
Website cookie data provides insights that are useful in boosting marketing success rates.
Mobile Device Data
Mobile devices are the most popular gadgets for accessing apps and sites. This makes cookies stored on these devices are invaluable to tracking consumer behavior. A mobile device provides critical data about a user’s:
- Communications
- Activities
- Mobile purchases
- Search and navigation history
- Social media clicks
- Check-ins, etc.
Geographic Location
Identifying where consumers come from is important for delivering relevant ads. DMPs are useful for recording and identify where a visitor’s IP address is from.
Demographics
In behavioral targeting, DMPs and other marketing programs collect demographic segmentation data, like:
- Gender
- Age ranges
- Interests, etc.
This information is used to create more personalized campaigns. Successful behavioral targeting relies on a quality data management platform to gather data.
Behavioral Targeting VS Contextual Targeting

What are the differences between behavioral targeting and contextual targeting?
Contextual targeting only shows users, ads that relate to the content of the site they’re on. This method does not take customer information into account. This means the ads visitors see may not always be relevant to their interests.
Behavioral Targeting shows users ads that fit their interests regardless of the content of the website they are on. When it comes to ad relevance and user experience, behavioral targeting is superior to contextual targeting.
Behavioral advertising’s only downside is that it requires investing in a reputable DMP for data collection. But, contextual and behavioral targeting aren’t completely exclusive. Behavioral targeting can be used to improve contextual targeting ads.
FAQs about behavioral targeting
1. What is behavioral targeting, and how does it work?
Using the information on user behavior, such as search history, browsing habits, and purchasing patterns, behavioral targeting is a marketing tactic that shows people tailored advertisements.
In order to serve advertisements that are more relevant and customized to the user, this targeting collects information on user behavior and uses algorithms to evaluate it in order to find trends and preferences.
2. What are the benefits of using behavioral targeting in advertising?
Because it enables marketers to provide ads that are more relevant to the user’s interests and choices, behavioral targeting can result in more efficient and effective advertising.
This can raise the probability that viewers will interact with the advertisement and carry out the targeted activity, such as visiting a website or making a purchase.
In addition, behavioral targeting can lessen wasteful advertising and boost return on investment (ROI).
3. How is behavioral targeting different from other types of targeting, such as demographic or geographic targeting?
Demographic targeting employs data on the user’s age, gender, and other attributes, whereas behavioral targeting concentrates on user activity, such as browsing and purchase history.
On the other side, geographic targeting picks out users according to where they are.
Because it targets users based on their interests and preferences rather than just their demographics or location, behavioral targeting is frequently considered to be more effective.
4. What data is used to target users behaviorally, and how is it collected?
Search searches, purchase histories, browsing patterns, and social media activity are among the types of information utilized for behavioral targeting.
This data is typically collected through cookies or other tracking technologies that monitor user behavior on websites and mobile apps.
5. What are some common privacy concerns associated with behavioral targeting, and how can they be addressed?
The gathering and use of personal data, the possibility of data breaches, and the use of data for unintended reasons are all privacy issues connected to behavioral targeting.
Businesses can allay these worries by being open about how they gather and utilize customer data, asking for permission before collecting data, and giving customers the chance to opt out of behavioral targeting.
6. How can businesses ensure that they are using behavioral targeting in an ethical and transparent manner?
Businesses should be forthright with consumers about their data collection and use practices, present users with clear and easy-to-understand privacy rules, and acquire user consent before collecting and using data if they want to employ behavioral targeting in an ethical and transparent way.
Businesses should also take responsibility for any breaches or exploitation of customer data and only use data for the intended purpose.
7. How can behavioral targeting be used to improve the user experience, rather than just serving ads?
The user experience can be enhanced by using behavioral targeting to deliver more pertinent and personalized content, such as product recommendations and useful resources.
Businesses may create a more engaging and rewarding user experience that fosters trust and loyalty by creating content that is tailored to the user’s interests and preferences.
8. What are some potential risks of using behavioral targeting, such as biases or unintended consequences?
Inaccuracies in the algorithms used to evaluate user data, the possibility of data breaches and unauthorized access to user data, and unintended repercussions, such as the manipulation of user behavior, are all potential hazards associated with behavioral targeting.
Companies need to be aware of these dangers and take precautions to reduce them, including routine targeting algorithm audits and the implementation of stringent data security policies.
9. What are the best practices for implementing a successful behavioral targeting campaign?
Clear goals and objectives, a defined target audience, the use of high-quality data and targeting algorithms, the creation of personalized and pertinent ad content, and ongoing campaign monitoring and optimization are all best practices for putting into action a successful behavioral targeting campaign.
10. How can businesses measure the effectiveness of their behavioral targeting efforts, and what metrics should they be looking at?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) like click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and return on ad spend can be used by businesses to gauge the success of their behavioral targeting strategies (ROAS).
They can assess the effectiveness of various targeting tactics and ad content using technologies like A/B testing and multivariate testing.
Businesses can also watch user activity and engagement with their ads using analytics tools, and then use that information to improve their targeting and content strategies.
Ending thoughts on the importance of behavioral targeting
Behavior-targeted ads improve a company’s ROI, click-through, and conversion rates. Today, behavioral targeting is critical to a company’s marketing success.
Overusing a customer’s personal information is risky. But, this doesn’t hinder the effectiveness of behavioral targeting.
If you leverage the behavioral targeting principle, you will attract and secure your customers. So, use a reputable data management platform to collect behavioral data and segment your audience. By doing this, you will reap increased profits and conversion rates on your onsite and offsite marketing campaigns.
If you enjoyed reading this article on behavioral targeting, you should check out this one about personalization algorithms.
We also wrote about a few related subjects like MVP tests, how to hire a web development team, software development budget, financial projections for startups, financial software development companies, proof of concept vs prototype, and lean software development principles.
- What Are Third-Party Cookies and How They Work - April 20, 2024
- How Do Websites Detect Adblock? It’s Quite Simple, Actually - April 14, 2024
- Financial Software Development Companies You Should Know - April 11, 2024